Newton S Second Law Of Motion Formula Derivation

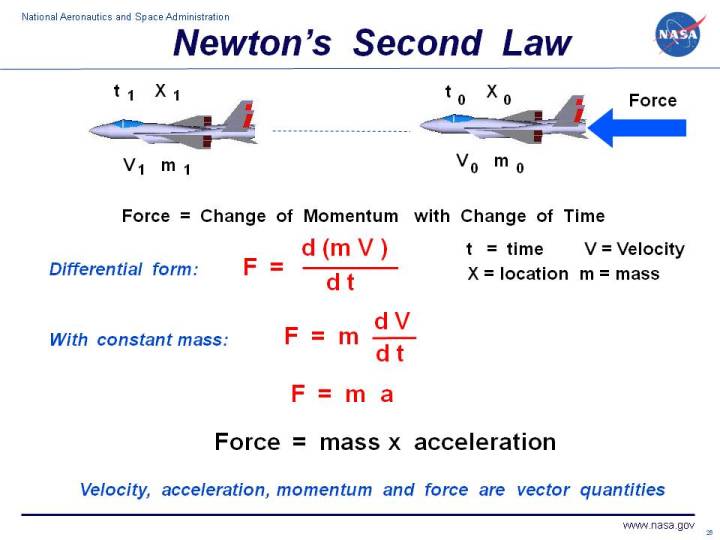
The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force in the same direction as the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Newton s second law of motion formula derivation. For a constant mass m newton s second law looks like. This then completes the derivation of e mc 2 for a body at rest. For a moving body its total energy is given by. The second law then reduces to the more familiar product of a mass and an acceleration.
Derivation of second equation of motion. F m a remember that this relation is only good for objects that have a constant mass. S ut a 2. Newton s second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object.
F m dv dt the derivative of velocity with respect to time is the definition of the acceleration a. If a body has a net force acting on it it is accelerated in accordance with the equation. Newton s second law is one of the most important in all of physics. The acceleration a of a body is directly proportional to the acting force f and inversely proportional to its mass m that is a f m or f ma m d2r dt2.
Newton s second law of motion can be formally stated as follows. Using newton s second law of motion force f can be shown as. Derivation of second equation of motion by algebraic method. Newton s law can be written as either f m δ v δ t.
The equation is also derived without calculus on this page. Thus the equation for kinetic energy k can now be shown as. Note that the velocity limit is c. A force applied to a body can change the magnitude of the momentum or its direction or both.
Consider the same notations for the derivation of the second equation of motion by the simple algebraic method. Newton s second law cannot be derived and is a statement of real physical content hence it is called a law. Often expressed as the equation a fnet m or rearranged to fnet m a the equation is probably the most important equation in all of mechanics. Newton s second law of motion newton s second law establishes a relationship between the force f acting on a body of mass m and the acceleration a caused by this force.
Newton s second law the second law of motion states that the acceleration of a moving body depends upon the mass of the object as well as the force acting on the object. For a body whose mass m is constant it can be written in the form f ma where f force and a acceleration are both vector quantities.