Newton S Second Law Of Motion Definition Simple

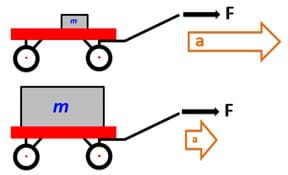
In the second law of newton known as the fundamental principle of dynamics the scientist states that the larger the mass of an object the more force will be required to accelerate it.
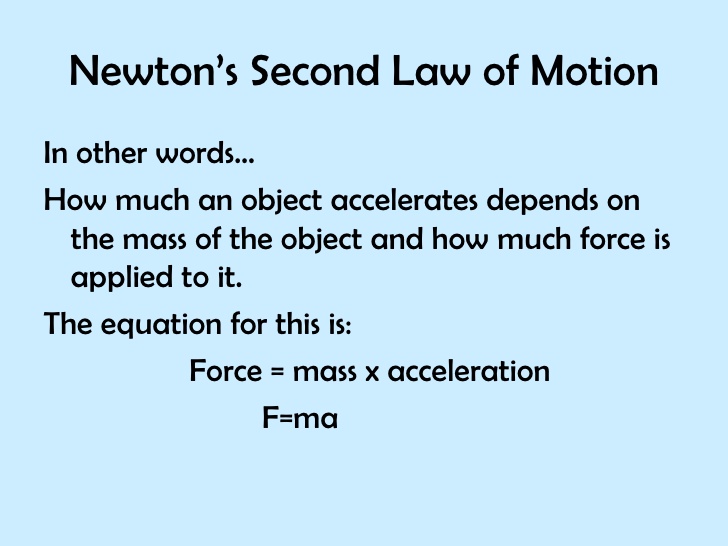
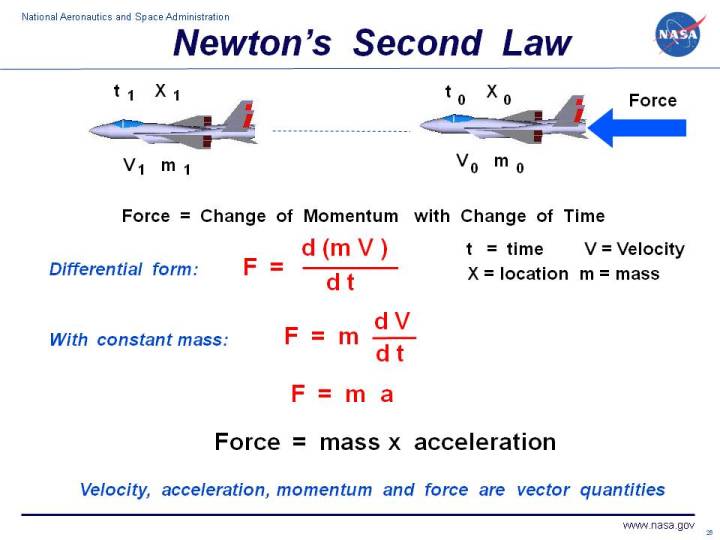
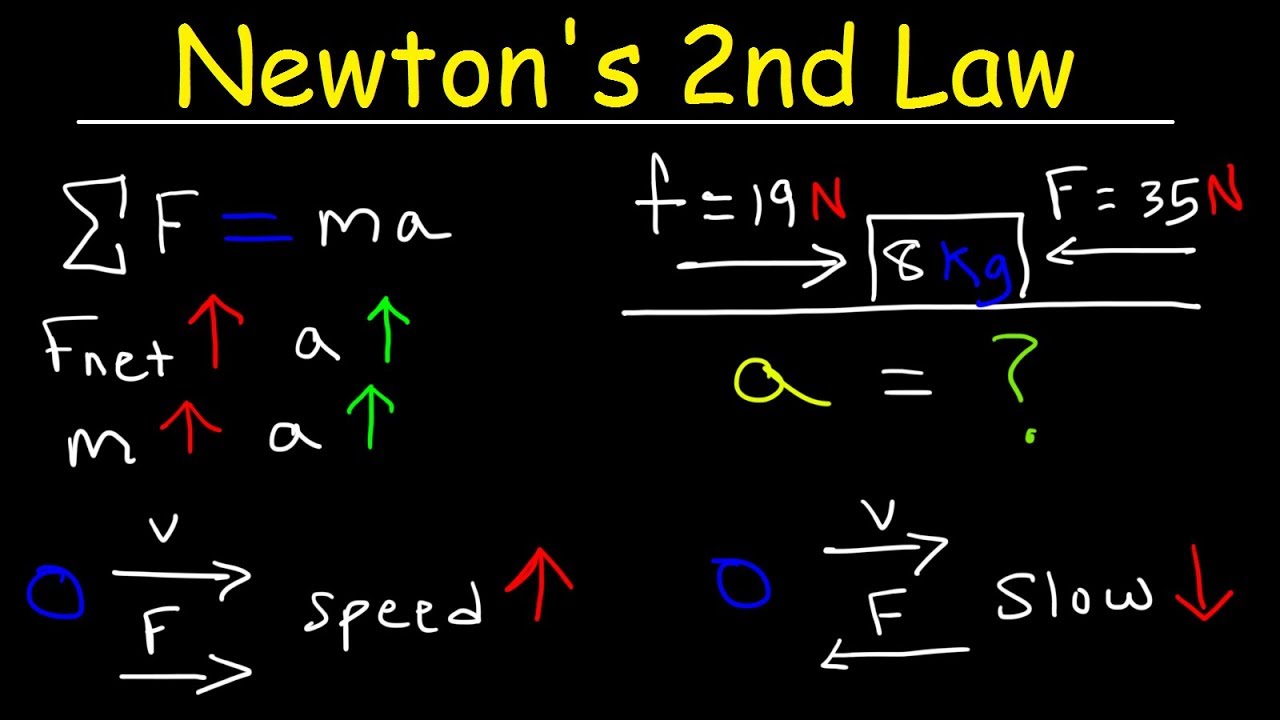
Newton s second law of motion definition simple. Displaystyle mathbf f m mathbf a. Expressed mathematically f ma where f is the force in newtons m is the mass of the body in kilograms and a is the acceleration in meters per second per second. The momentum of a body is equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. F m a.
The principle stating that a force acting on a body is equal to the acceleration of that body times its mass assuming a constant mass. A equals start fraction sigma f divided by m end fraction. Newton s second law of motion can be stated as. Newton s second law states that acceleration of a particle is dependent on the forces acting upon the particle and the particle s mass.
For a particle of mass m the net force f on the particle is equal to the mass m times the particle s acceleration a. That is the acceleration of the object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to that of the object. Newton s second law of motion. It states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it.
The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. After isaac newton. Newton s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. Is the mass of the object.
We know objects can only accelerate if there are forces on the object. Newton s second law tells us exactly how much an object will accelerate for a given net force. This law may be written as force mass x acceleration or. Newton s second law of motion states that when a force acts on an object it will cause the object to accelerate.
Newton s second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied and this change in momentum takes place in the direction of the applied force. Expanding newton mechanics with neutrosophy and quad stage method new newton mechanics taking law of conservation of energy as unique source law. The relationship between an object s mass m its acceleration a and the applied force f is f ma.